Get ready to dive into the world of Best Credit Unions vs Banks! This comparison will unveil the differences in services, fees, and customer experiences, providing you with a comprehensive look at your financial options.
As we explore the realm of credit unions and banks, you’ll discover a treasure trove of information that will help you make informed decisions about where to entrust your hard-earned money.
Best Credit Unions vs Banks
Credit unions and banks both offer financial services to customers, but there are key differences between the two in terms of services, fees, interest rates, eligibility requirements, and customer service experiences.
Services Offered
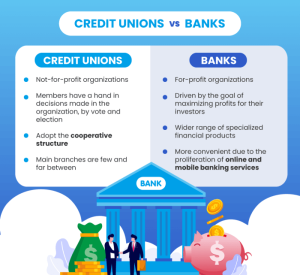
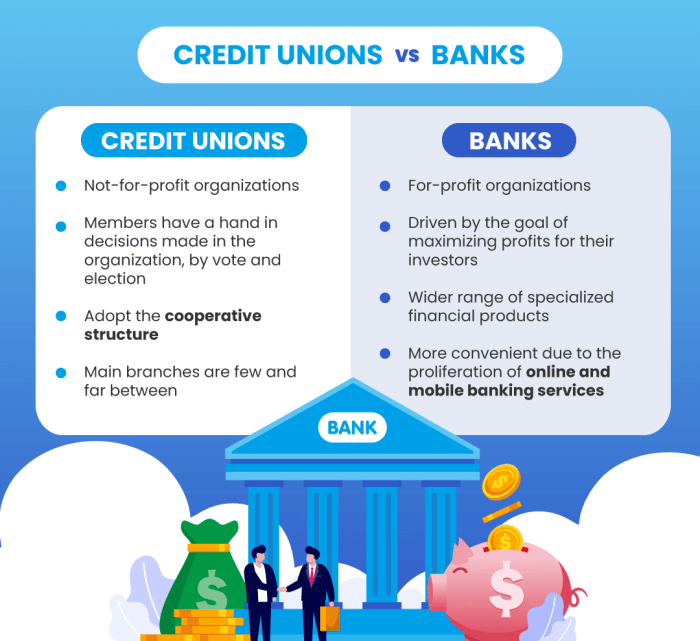
- Credit Unions: Credit unions are not-for-profit organizations owned by their members, offering similar services to banks such as savings accounts, checking accounts, loans, and credit cards. They may also provide personalized financial advice and guidance.
- Banks: Banks are for-profit institutions that offer a wide range of financial services, including savings accounts, checking accounts, loans, credit cards, investment services, and wealth management.
Differences in Fees and Interest Rates
- Credit Unions: Credit unions typically have lower fees and higher interest rates on savings accounts and loans compared to banks. This is because they are member-owned and operate on a not-for-profit basis.
- Banks: Banks may have higher fees and lower interest rates on savings accounts and loans due to their for-profit nature and operational costs.
Eligibility Requirements
- Credit Unions: To join a credit union, individuals must meet specific membership criteria, which can include living in a certain geographic area, working for a particular employer, or belonging to a specific organization.
- Banks: Opening an account at a bank is generally more accessible, as banks do not have membership requirements like credit unions. Customers typically only need to provide identification and meet basic account opening criteria.
Customer Service Experiences
- Credit Unions: Credit unions are known for their personalized customer service, as they prioritize building relationships with their members. Customers often feel more valued and supported by the staff at credit unions.
- Banks: Banks may offer a wider range of services and digital banking options, but customer service experiences can vary. Some banks focus on providing excellent customer service, while others may fall short in this area.
CREDIT AND COLLECTIONS BANKING SERVICES

Credit and collections are essential components of banking services that involve managing credit risk and recovering outstanding debts. These services play a crucial role in maintaining the financial health of a bank by ensuring timely repayments and minimizing default risks.
Define Credit and Collections
Credit refers to the provision of funds or financial resources to individuals or businesses with the expectation of repayment with interest. Collections, on the other hand, involve the process of recovering overdue payments from borrowers who have failed to meet their repayment obligations.
Credit Assessment Process
- For Individuals: Banks assess an individual’s creditworthiness based on factors such as credit history, income level, employment status, and existing debts. This information helps determine the individual’s ability to repay the loan.
- For Businesses: Banks evaluate a business’s creditworthiness by analyzing financial statements, cash flow projections, business history, and market conditions. This assessment helps banks determine the risk associated with lending to the business.
Strategies for Debt Collection
- Banks may employ internal collection departments or outsource debt collection to third-party agencies to recover overdue payments.
- Communication with delinquent borrowers through phone calls, letters, and emails is a common strategy used by banks to remind borrowers of their outstanding debts.
- Banks may also offer repayment plans or negotiate settlements with borrowers to recover the overdue amount while maintaining a positive relationship.
Impact on Financial Health
- Effective credit and collections services help banks minimize credit losses, improve cash flow, and maintain a healthy loan portfolio.
- Timely debt collection ensures that banks can recover funds to meet their financial obligations and maintain liquidity.
- Poor credit management and collections practices can lead to increased non-performing loans, higher provisions for bad debts, and ultimately impact the profitability and stability of a bank.
Last Recap

In conclusion, whether you choose a credit union or a bank, understanding the nuances between them is key. With this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the financial landscape and make the best choice for your individual needs.
Question Bank
What are the main differences between credit unions and banks?
Credit unions are member-owned, not-for-profit organizations, while banks are for-profit institutions owned by shareholders. Credit unions typically offer higher interest rates on savings accounts and lower fees compared to banks.
How do eligibility requirements differ for credit unions and banks?
Credit unions usually have specific membership criteria, such as being part of a certain community or organization, whereas banks are generally open to anyone who meets their account opening requirements.
What can I expect in terms of customer service at credit unions versus banks?
Credit unions are known for their personalized service and community focus, often providing a more hands-on approach to banking. Banks, on the other hand, may offer more convenience in terms of branch locations and online services.